December 01.2025
Microphone Welding Machine Solution
| 01 | |
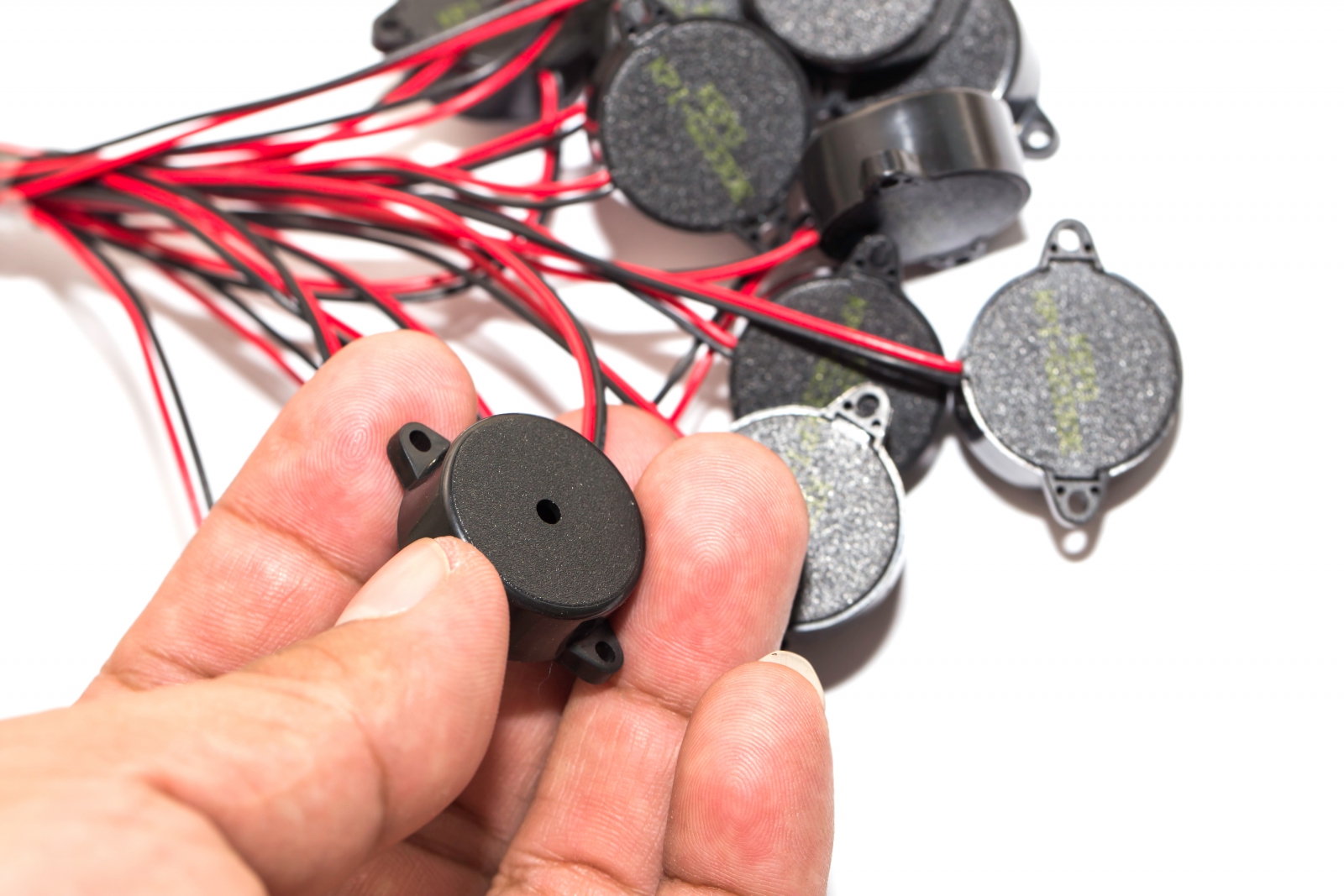
| Project Background The rise of microphone welding machine projects is directly linked to the miniaturization of modern consumer electronics and the rapid growth in acoustic demands. With the widespread adoption of products such as TWS earphones, smart wearable devices, and smartphones, the number of microphones integrated into these devices continues to increase, while their size becomes increasingly tiny, often measuring only a few millimeters square. This extreme miniaturization poses significant challenges to traditional manufacturing processes. As a highly precise acoustic component, the internal diaphragm and coil of a microphone are highly sensitive to temperature. Traditional soldering iron methods, due to their prolonged contact time and high heat conduction, can easily damage the microphone from overheating, leading to reduced sensitivity or complete failure, resulting in substantial quality costs. At the same time, the microphone's leads are as fine as hair, and its solder pads are extremely small. Prolonged repetitive manual operations make it difficult to ensure precise alignment and consistent soldering, leading to low production efficiency, unstable yield rates, and rising labor costs. Existing general-purpose automatic soldering equipment often falls short in positioning accuracy, visual recognition, and thermal control when dealing with the precision welding of such ultra-miniature, heat-sensitive components. Meanwhile, imported high-end specialized equipment comes with limitations such as higher costs, longer delivery times, and inconvenient service support. Therefore, the market urgently requires an automated welding solution that can achieve high precision, non-contact operation, low thermal impact, and cost-effectiveness. This is precisely the core context behind the emergence of microphone welding machine projects. They aim to break through the current bottlenecks in the assembly of miniature acoustic components in the manufacturing industry by integrating advanced technologies such as visual positioning and laser welding, meeting the downstream industry's urgent need for improved efficiency, guaranteed yield rates, and optimized overall costs. | |
 | |
| 02 | |
| Efficient and Reliable Professional Solution | |
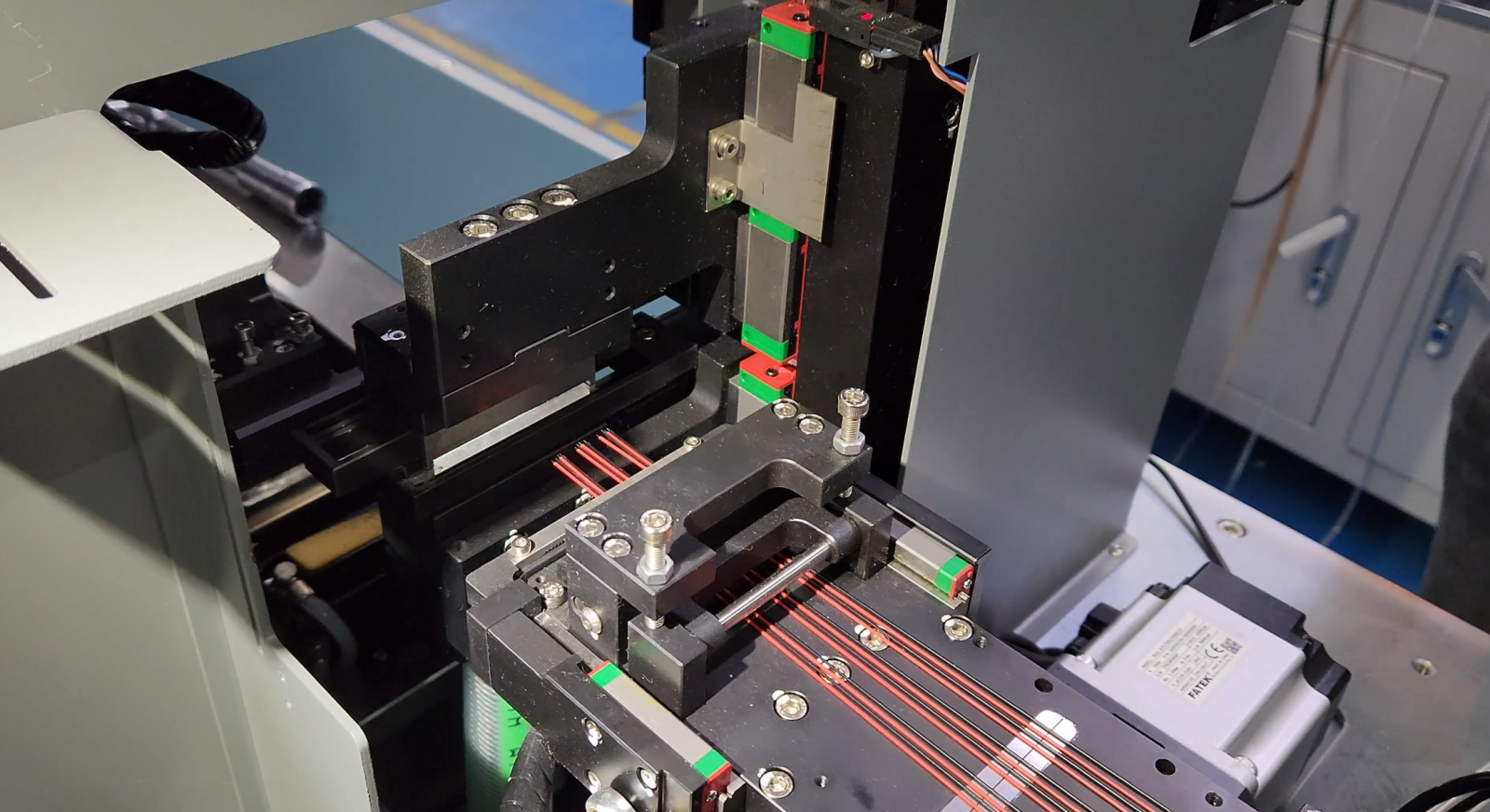
| According to the hardware configuration and functional requirements of the equipment, the control system adopts the FATEK M-series PLC, along with 5 DI/DO modules to meet diverse input/output needs. It supports up to 16 axes of bus-type servo drives and 4 axes of high-speed pulse output, enabling various motion control functions including point-to-point motion, multi-axis linear interpolation, circular interpolation, and continuous interpolation, achieving highly diversified motion control. For human-machine interaction, a FATEK P5B-series HMI touch panel is selected, allowing for more operable controls on a single screen. To meet the demands for high precision and rapid response in motion positioning during the equipment's production process, the entire microphone welding machine utilizes the FATEK SC3-series EtherCAT bus servo drive system, with motor products selected to match the different execution modules, balancing performance and power consumption. | |
 |
| 03 | |
| FATEK Makes You Stand Out
► Automatic Wire Discarding ► Selective Crimping ► High-Efficiency Response ► Dual-Station Feeding/Welding | |
| 04 | |
| FATEK Products Selected in the Solution |

